Unlocking the Quantum Realm: Journey into the Future of Computing
-
- Information
-
Who is online
Users browsing this forum: No registered users and 16 guests
Recent Posts

Microsoft Introduces Semantic Search for Windows 11 Insider Preview on Snapdragon PCs
Tue Jan 21, 2025 12:08 pm
priyasng
135
2

MagicOS 9 Update for HONOR Magic 6 Pro: A Comprehensive Breakdown
Fri Jan 03, 2025 12:15 am
SudhanshuRoy
7688
12

A Deep Dive into the Dark Web: What It Is, Its Risks, and Misunderstandings
Wed Jan 22, 2025 9:50 pm
CtrlAltWin
59
1

Security Researcher Discovers High-Severity Vulnerability in ChatGPT API
Wed Jan 22, 2025 11:48 am
priyasng
72
1
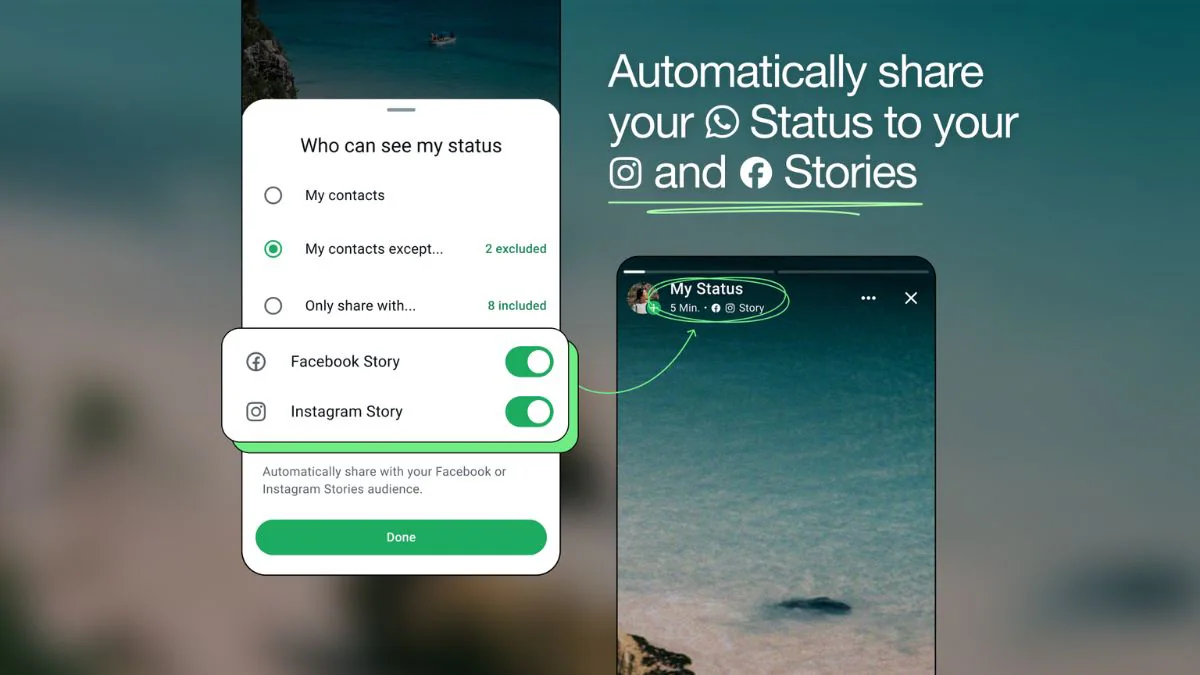
WhatsApp to Integrate with Meta Accounts Centre for a More Connected Experience
Wed Jan 22, 2025 11:38 am
priyasng
72
1

How to Set Up a Smart Home Ecosystem: A Beginner’s Guide
Tue Jan 21, 2025 2:26 pm
CtrlAltWin
131
1
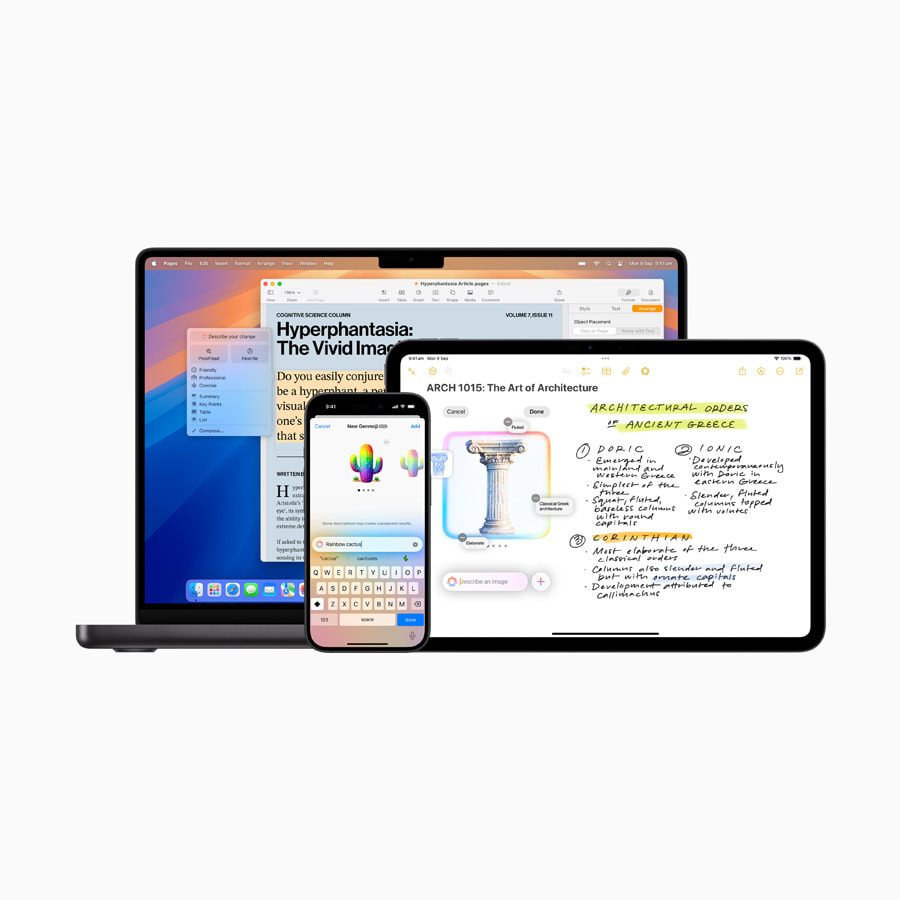
Apple Temporarily Disables Notification Summaries Feature for News and Entertainment Apps in iOS 18.3
Fri Jan 17, 2025 5:15 pm
priyasng
206
1

OpenAI’s new ‘Tasks’ tool could make ChatGPT your daily sidekick
Wed Jan 15, 2025 5:16 pm
CtrlAltWin
147
1

AI Could Soon Shatter Advanced Security in Seconds, Warns NATO-Backed Startup
Thu Jan 09, 2025 4:28 pm
CtrlAltWin
650
2

WhatsApp Web to Introduce 'Chat with Us' for Quick Support, AI-Powered Responses in Development
Mon Dec 30, 2024 4:47 pm
priyasng
1681
2
- Copyright © 2024 Magicnation. All rights reserved.
