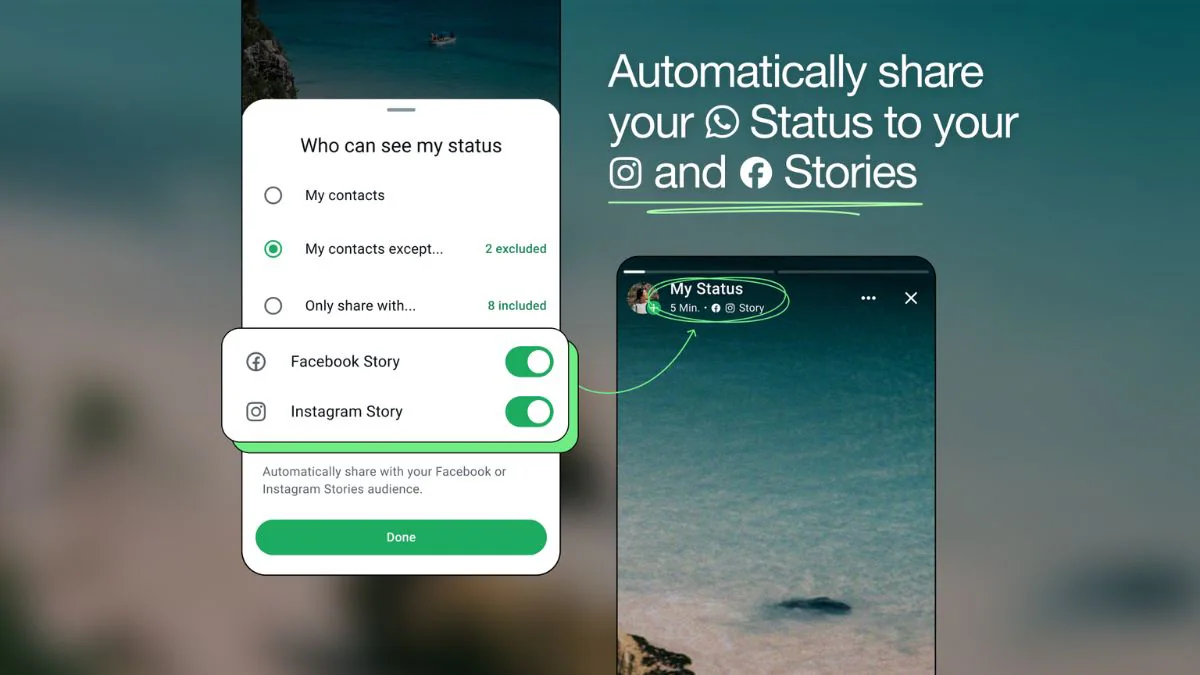
What Are Biometric Payments?
Biometric payments leverage an individual’s biological features to verify their identity and authorize transactions. Unlike traditional payment methods that require cards, PINs, or passwords, biometric systems use data that is unique to each person, such as:
- Fingerprints
- Facial features
- Iris patterns
- Voice recognition
How Do They Work?
Biometric payment systems follow a simple process:
Users register their biometric data (like a fingerprint or facial scan) with a payment system or financial institution.1. Enrollment:
The biometric data is securely stored as encrypted templates, often in the device itself or a secure database.2. Storage:
During a transaction, the system scans the user’s biometric feature and compares it to the stored template. If they match, the payment is authorized.3. Authentication:
The process is seamless, taking only seconds to complete.
The Benefits of Biometric Payments
Forget fumbling for your wallet or remembering passwords. With biometric payments, all you need is yourself—no cards or devices required.1. Convenience:
Biometric data is unique and difficult to forge, making it a more secure alternative to PINs or passwords that can be stolen or guessed.2. Enhanced Security:
Biometric systems streamline transactions, reducing checkout times and improving customer experience.3. Speed:
By tying transactions to a person’s physical identity, biometrics reduce the risk of identity theft and fraudulent transactions.4. Reduced Fraud:
Biometric payments can benefit people without access to traditional banking, as they don’t require physical cards or extensive documentation.5. Inclusivity:
Challenges and Concerns
Despite its benefits, biometric payment systems face several challenges:
Storing and managing sensitive biometric data raises concerns about privacy and potential misuse. If a database is hacked, recovering stolen fingerprints or facial data isn’t as simple as resetting a password.1. Privacy Concerns:
Implementing biometric systems can be expensive for businesses, particularly small retailers.2. Cost:
While highly reliable, biometric systems aren’t foolproof. Factors like poor lighting or injuries can interfere with scans.3. Accuracy Issues:
Who owns your biometric data—the user, the financial institution, or the technology provider? This question remains a significant legal and ethical issue.4. Data Ownership:
Real-World Applications
Biometric payments are already being adopted around the world.
- Smartphones and Wearables:
- Retail POS Systems:
- Banking:
- Transportation:
The Future of Biometric Payments
As technology evolves, biometric payments are expected to become even more sophisticated. Innovations like heartbeat recognition, vein mapping, and behavioral biometrics could offer additional layers of security and convenience.
However, widespread adoption will require addressing privacy concerns, ensuring interoperability across devices and systems, and making the technology affordable for businesses of all sizes.
Biometric payments have the potential to transform the way we transact by making payments faster, safer, and more convenient. While challenges like privacy and cost remain, the benefits of this technology are undeniable.
As we move toward a cashless, cardless society, biometrics could very well become the standard for how we pay—turning science fiction into everyday reality.